Education system structure
According to the Education Code, the education system in Moldova is organised by levels and cycles in accordance with the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED-2011), and has the following structure:
-
ISCED 0 - early education: pre-primary education; preschool education;
-
ISCED 1 - primary education;
-
ISCED 2- lower secondary education, cycle I: gymnasium education;
-
ISCED 3: upper secondary education, cycle II: lyceum education; secondary technical and vocational education and training;
-
ISCED 4 - post-secondary technical and vocational education and training;
-
ISCED 5 - post-secondary non-tertiary technical and vocational education and training;
-
ISCED 6 - higher education, cycle I: bachelor’s degree;
-
ISCED 7 - higher education, cycle II: master’s degree;
-
ISCED 8 - higher education, cycle III: doctoral degree
-
Adult education
Compulsory education begins with the preparatory group of preschool education and ends with secondary education.
The obligation to attend compulsory education ends at the age of 16.
The responsibility for the compulsory schooling of children up to the age of 16 rests with the parents or other legal representatives and the local public administration authorities of the first and second levels.
The Ministry of Education and Research elaborates, approves and monitors compliance with the regulations for compulsory enrolment of school-aged children.
The education system of the Republic of Moldova can be graphically represented, in the following way:
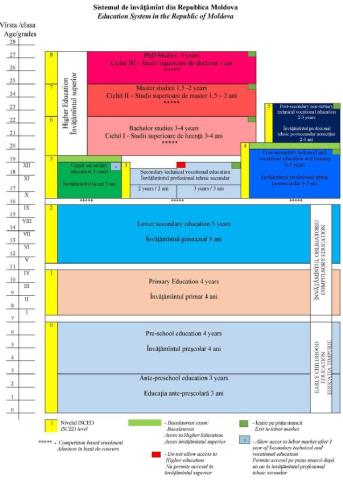
Source: ENIC-NARIC
Types of education/training institutions
According to the education structure, educational institutions are classified as follows:
-
pre-primary education institution – nursery, community centre for early education;
-
preschool education institution– kindergarten, community centre for early education;
-
primary education institution – primary school;
-
secondary education institution, cycle I – gymnasium;
-
secondary education institution, cycle II – lyceum;
-
general education institution with combined programmes – educational complex (primary school-kindergarten, gymnasium-kindergarten);
-
institution of secondary technical and vocational education and training - vocational school;
-
institution of post-secondary and post-secondary non-tertiary technical and vocational education and training – college;
-
institution of technical and vocational education and training with combined programmes – centre of excellence;
-
secondary vocational education institution for arts, sport etc. ─ school;
-
higher education institution – university, academy of studies, institute, high school, school of higher studies and others;
-
specialised education institution for continuous training – university, institute, center, school, etc.;
-
institution of extra-school education – school (of arts, music, theatre, sport, etc.), creation centre, sport club, sports center for national teams training, rest camp;
-
institution of special education – special school, auxiliary school.
In case the educational institution offers study programmes of several levels and has a single management and administration, it will be named after the highest educational level provided.
Depending on the type of ownership, the educational institutions are classified as follows:
a) public education institution;
b) private educational institution.
Home education
The organisation of home education in the Republic of Moldova is regulated by - the Education Code, as well as by the Instruction on the organisation of home education.
The purpose of home education in the Republic of Moldova is to ensure the right to education for the pupil unable to attend the educational institution.
Home education is organised for a specific period, for children and pupils who, due to health problems or a disability, are temporarily deprived of the possibility to move.
Home education monitoring is carried out at several levels:
-
At the central level – by the Ministry of Education and Research and the Republican Center for Psycho-pedagogical Assistance,
-
At the district level - by the local specialised body in the field of education of the local public administration and UTA Gagauzia,
-
At the local level – by the educational institution.
The process of organising education at home involves carrying out the complex evaluation of the child's development and participation capacity, issuing the decision of the local specialised body in the field of education and ensuring the implementation of the individual educational process by the educational institution.
The complex evaluation of the child's development is carried out by the Psycho-pedagogical Assistance Service, based on the referral of the case by the educational institution, certain institutions and structures in the field of protection and support for the child or directly by parents/ child (16-18 years) request.
As a result of the complex evaluation, the Psycho-pedagogical Assistance Service prepares a Report, which contains the appropriate conclusions and recommendations, as well as the general conclusion of identification/non-identification of special educational requirements, the reassessment period, the form of inclusion and support services.
The decision regarding the organisation of individual education at home is confirmed by the order of the local specialised body in the field of education.
In the case of children with disabilities, the order is issued based on the request of the child's parents/legal representatives, to which is attached:
-
the complex assessment report for the child's development drawn up by the Psycho-pedagogical Assistance Service,
-
the disability and work capacity certificate and the individual rehabilitation and inclusion programme social certificate issued by the National Council for Determining Disability and Working Capacity or its territorial structures.
In the case of other children, the order is issued based on the conclusion of the attending physician, confirmed by the signature of the head of the medical and sanitary institution at the place of residence.
The educational institution in the locality/district where the respective pupil is located organises home education, approves the schedule and monitors the activity of teaching staff at the pupil's home.
The lesson schedule, coordinated with the child's parents, is approved by the Administrative Council of the educational institution, until the start of the school year or no later than two weeks after issuing the order of the local specialised body in the field of education regarding the organisation of home education.
The organisation of the educational process at home for the pupil who completes the subjects of study based on the general curriculum for primary, secondary or lyceum education, is carried out on the basis of the Education Plan drawn up by the deputy director responsible for the training activity, approved by the head of the institution.
The organisation of the educational process for the primary or secondary school pupil, who completes the subjects of study based on the adapted/modified home education curriculum, is organised in accordance with the individualised educational plan, developed and approved in the manner established by the Ministry of Education.
By the decision of the Teacher's Council, the educational process at home for the lyceum education pupil can be organised, for one or more subjects included in the home education plan, based on the general curriculum, through distance education, in accordance with the normative provisions in force, provided that the educational institution provides the necessary equipment.
The home-schooled pupil is registered in the class Catalogue, in which the semester and annual average marks for the subjects of study, the mentions regarding the promotion from class to class or the graduation of the level of education are entered.
For the home-schooled pupil, an individual register is drawn up in which the records of the lessons, the lessons taught and the results/grades of the current, thematic and final evaluations for the study subjects according to the individual education plan are entered.
The evaluation of school results, with the objective of evaluating the level of development of the pupil's skills, is carried out based on the state educational standards or the Individualiszed Educational Plan.
The secondary and lyceum graduation exams, organised through individual education at home, are conducted based on the provisions of the normative acts developed by the national entity with evaluation and examination functions and approved by the Ministry of Education.
The pupil, for whom education at home is established, can benefit from support services, recommended by the regional/municipal psycho-pedagogical assistance service based on the complex assessment report of the child's development and included in the individualised educational plan.
The pupil with home education can be included in non-formal educational activities, including socialisation, with the involvement of other people (relevant specialists active in the locality: from the field of health/social assistance/culture, pupils, students, etc.), volunteering based, with the consent of the parents. The educational institution will monitor the voluntary activity of pupils and students.
The administration of the educational institution organises and monitors the conduct of home lessons in accordance with the approved timetable, the implementation of the curriculum and provides methodological assistance to the specialists who carry out home education.
The financing of individual education at home is carried out from the budget of the educational institution, calculated on the basis of the standard cost per pupil, in accordance with the procedures established in the normative acts in force.
If the child's residence is in a different locality than the one in which the educational institution is located, the teaching staff is provided with transport or travel expenses reimbursement.

