Address
Nacionalinė Švietimo Agentūra
The National Agency for Education
Eurydice Unit
K. Kalinausko str. 7
LT-03107, Vilnius
Tel: +370 658 18124
E-Mail: info@nsa.smm.lt
Website
2025
An update of the Matrura Certificate in 2025
According to the Procedure for the Issuance of Certificates and Matura Certificates, from 1 February 2025, Lithuanian school graduates who have acquired secondary education (after completing the secondary education curriculum) and have passed at least two state Matura examinations (Lithuanian language and literature plus one self-selected) will be issued certificates in this updated format.
2024
From 2024, Lithuanian school graduates who pass the Matura examinations will receive a digital Matura Certificate in Lithuanian and English.
This is enshrined in the amended Procedure for the Issuance of Certificates and Matura Certificates which entered into force on 15 May 2024.
The Matura Certificates can be accessed (viewed, downloaded and printed) at the Register of Diplomas, Certificates and Qualifications. Certificates are deemed to have been issued when registered in the Register of Diplomas, Certificates and Qualifications (including a registration number) after the school prepares these certificates.
To have the Matura Certificate approved by a notary public, it must first be downloaded and printed from the Register of Diplomas, Certificates and Qualifications and signed by the school principal, either by hand or electronically, and stamped with the school seal. Afterwards, a notary public certifies the Matura Certificate by issuing the Apostille.
The amended procedure has also changed the form of the certificate of learning achievement issued to a person holding the Matura Certificate who has additionally taken or retaken the Matura Exams (to obtain a higher score), and/or completed the specific subject course (to obtain a higher annual evaluation).
Procedure for suspending schools failing to achieve criteria
A government decision adopted at the end of 2024 states that a school’s general education programme, or part of it, can be suspended if it fails to meet at least one of the criteria for such programmes and the school is unable to correct the deficiencies within a year. General, specific and additional criteria for school performance are set out in the Law on Education. Their quantitative and qualitative meanings are set out in the Rules on the Establishment of the School Network approved by the government.
These procedures will apply to both state and non-state schools. If a school is found not to meet some of the criteria, a time limit (up to one year) will be set in which to remedy the deficiencies. If the school fails to correct the identified deficiencies within the deadline, it would be closed and the pupils would have to be transferred to another school.
2023
Stricter measures to enforce school attendance
Amendments to the Law on Education have strengthened the enforcement of school attendance.
Schools must inform parents/guardians on the same day of any absence—from school or an individual lesson—of a pupil enrolled in a general education programme, unless the parents/guardians have notified the school in advance of the child’s absence. The law also imposes an obligation on the school to inform the state’s Child Rights Protection and Adoption Service under the Ministry of Social Security and Labour, of cases where the parents (guardians, or custodians), do not ensure the child’s obligation to attend school until the age of 16.
As of 1 September, parents are legally required to explain up to five days per month due to illness. If more days are missed, a document justifying the pupil’s illness or a visit to the doctor is required.
Unified admissions system
Amendments to the Law on Education changed the way applications for admission are submitted, moving from the previously decentralised, district-by-district practice to a single, online application platform.
The public body, Mokausi Lietuvoje, will administer a centralised admissions system for all pre-school, pre-primary, primary, lower secondary, upper secondary, non-formal children’s education, and formal, supplementary education programmes. As there will be no more paper applications, those who do not have a computer or other facilities at home will be able to submit their applications through the systems available in the municipality.
The platform will also provide information on education providers, education programmes, admission conditions and the results of admissions.
Since 1 May 2023, digital certificates, including Matura certificates, are being issued in Lithuania
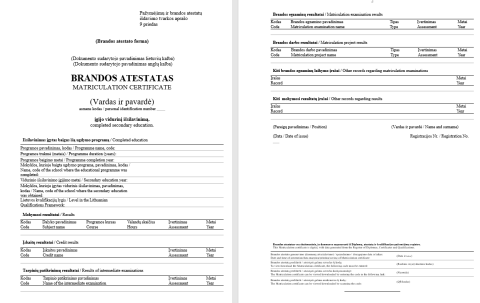
General education certificates and maturity certificates are issued in the Republic of Lithuania according to the Order of the Minister of Education, Science and Sport On the Approval of the Procedure for the Issuance of Certificates and Matura Certificates.
Digital (electronic) certificates and matura certificates are prepared based on the information system tools of the Register of School Pupils and the Register of Diplomas, Certificates and Qualifications, and are accessible (can be viewed, downloaded from an email and/or printed) in the Register of Diplomas, Certificates and Qualifications.
Certificates and maturity certificates are deemed to have been issued when they are registered in the Register of Diplomas, Certificates and Qualifications (including a registration number) after the school prepares the certificates. The school principal certifies the transfer of the data/records to the register with their electronic signature and is responsible for the accuracy of the data/records contained in the certificates and matura certificates.
A numerical code and a QR code are specified in the last table in the certificate and the matura certificate. The school is able to provide this code to the pupil if the pupil cannot access the Electronic Government Gateway to download (or view) their certificate and/or matura certificate. Other persons, national and foreign authorities, are able to check the fact of issuance of the certificate, the authenticity of the data, etc. by using the code and/or QR code with the consent of the owner of the certificate or matura certificate (login link: https://www.dakpr.smm.lt/aikos2-dakpr/edocSearch.xhtml) in accordance with personal data protection legislation.
More information on how to issue digital certificates and matura certificates, how to download, view or print the certificates and/or matura certificates, etc. for students and their parents/foster parents/guardians by logging into the information system of the Register of Diplomas, Certificates and Qualifications is available on the website of the National Agency for Education.
Form of Matura certificate