Address
Unité nationale d'Eurydice
ANEFORE ASBL
eduPôle Walferdange
Bâtiment 03 - étage 01
Route de Diekirch
L-7220 Walferdange
Tel: +352 247 85289
E-Mail:info@anefore.lu
Website: www.anefore.lu
Secondary and post-secondary education is managed on a central level by the ministry of Education, Children and Youth (MENJE; ministère de l’Éducation nationale, de l'Enfance et de la Jeunesse).
Secondary schools (lycées) have a certain degree of autonomy with regard to contents and teaching methods, organisation of teaching, and financial management. This relative autonomy allows lycées to address specific challenges related to the institution or their student population.
Structure of secondary education
The national public education system offers two main pathways of secondary education:
- Classic secondary education (ESC; enseignement secondaire classique) mainly prepares students to continue further studies in higher education and university
- General secondary education (ESG; enseignement secondaire général) is more vocationally oriented and prepares students, depending on the pathway chosen, either to continue their studies in higher technical education or to learn a trade via vocational education and training, or else to directly access the job market as qualified workers.
Several other organisational variations are also provided by the public education system in Luxembourg. These alternative pathways mainly aim at adapting the education provision to the linguistic and cultural diversity of Luxembourg's resident population. These variations are part and parcel of Luxembourg's public education system, and as such they are free of costs.
These alternatives are as follows:
- European education
- International education
- German-Luxembourgish education
- UK-style education.
These variations are described in sub-chapter 6.10 'Organisational variations and alternative structures'.
An overview of the full public education provision can be downloaded from the ministry of Education's website (cf. sub-chapter 2.3 'Learning opportunities in the public school system').
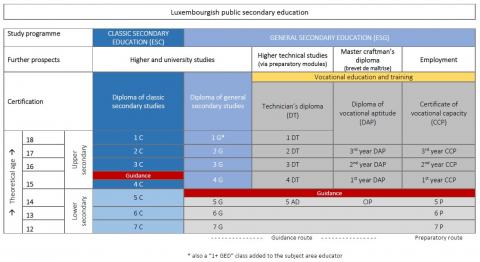
The diagram below shows the public secondary education provision in Luxembourg:
The Education ministry's publication on the schools' programme provision 'Offre scolaire 2021-2022' (in French) informs about the geographical location of the different establishments. It also details each school's educational offer.
In order to facilitate guidance and help students and parents find the best suitable school for the learners' aspirations and capacities, the ministry has also created a website Meng Schoul ('my School') with an interactive map. The establishments offering the programme of the learner's choice appear in answer to the criteria entered on the website (secondary education, vocational education and training and higher education).
ESC - Classic secondary education
(ESC; enseignement secondaire classique)
Classic secondary education imparts wide-ranging knowledge in humanities and social sciences, literature, mathematics and natural sciences and prepares students to higher education and university.
The standard study duration in ESC is 7 years.
Study years are named in descending order from 7e (septième), which is the first study year, through 6e (sixième), 5e (cinquième), 4e (quatrième), 3e (troisième), 2e (deuxième), downward to 1ère (première), which is the 7th and final year in ESC.
The structure of ESC comprises:
- Lower years: from grades 7e to 5e (with optional Latin as from 6e)
- Upper years: from grades 4e to 1ère (with a choice of section at the end of 4e).
The final certification of ESC is the classic secondary school leaving diploma (diplôme de fin d’études secondaires classiques), which allows access to higher education in all disciplines.
The secondary school leaving diploma includes a diploma supplement specifying the subjects studied in the two last years and the final marks obtained in the last.
ESG - General secondary education
(ESG; enseignement secondaire général)
General secondary education offers several learning pathways of technically-oriented education. According to the learning path chosen, students can prepare for studies in higher education or higher technical education, or directly for working life.
The standard study duration in ESG is 7 years (to obtain a secondary school leaving diploma or a DT technician's diploma), an additional 8th year being needed for diplomas in health professions and social professions). To obtain a vocational DAP diploma or a CCP certificate the standard study duration is 6 years.
Study years are named in descending order from grade 7e (septième), which is the first study year, through 6e (sixième), 5e (cinquième), 4e (quatrième), 3e (troisième), 2e (deuxième), downward to 1ère (première), which is the 7th and final year in ESG.
ESG comprises 3 years of lower secondary education and 3 to 4 years (respectively 5 for social & health professions) in the upper cycle.
Upper years (students aged 15 to 19) are divided into three regimes:
- Technical regime (régime technique) has a standard duration of 4 years (5 years for health and social professions) and leads to a genersl secondary school leaving diploma (diplôme de fin d’études secondaires générales) allowing access to higher education
- Technician’s regime (régime de la formation de technicien) of 4 years leading to a technician’s diploma (DT; diplôme de technicien) providing access to higher technical studies
- Vocational regime (régime professionnel) of 3 years, leading to either a vocational aptitude diploma (DAP; diplôme d’aptitude profesionnelle) granting job market access as a qualified worker; or a certificate of vocational ability (CCP; certificat de capacité professionnelle).
The upper classes of General secondary education are organised in 5 divisions:
- Administrative and commercial sector
- health and social sector
- General technical division
- Art professions
- Hotel and tourism sector.
These are subdivised themselves in sections. For more information, see the above-mentioned publication 'Offre scolaire 2021-2022' (in French).
Post-secondary non-tertiary education
Preparatory courses for the master craftsman’s diploma (brevet de maîtrise) are exclusively proposed by the chamber of Trade (Chambre des métiers). They are organised as formal courses outside the structure of education. The courses are aimed at future entrepreneurs and professionals who wish to take a position of responsibility in a craft, whether industrial or commercial.
The final degree is a comprehensive qualification recognised on the national level.
