In Denmark, the parents of the child are obligated to ensure their child's participation in the teaching provided by the Danish public school (Folkeskole) or the equivalent.
Education is compulsory between the age of six and 16. Compulsory education consists of ten years of primary and lower secondary education, including one pre-school year (form level 0) and nine school years (form level 1-9). It is optional to attend the tenth form.
Home education
Parents or guardians, who can teach or provide teaching comparable to the Folkeskole, can do so. To undertake home education, they submit a written declaration to their local municipal authorities that include information about which children that will be participating, where the teaching will take place, and who will be teaching the children.
The local municipality supervises the teaching of home-educated children and the municipality is entitled to test the children annually. Often, it is an employee from the educational-psychological advisory service that carries out the test.
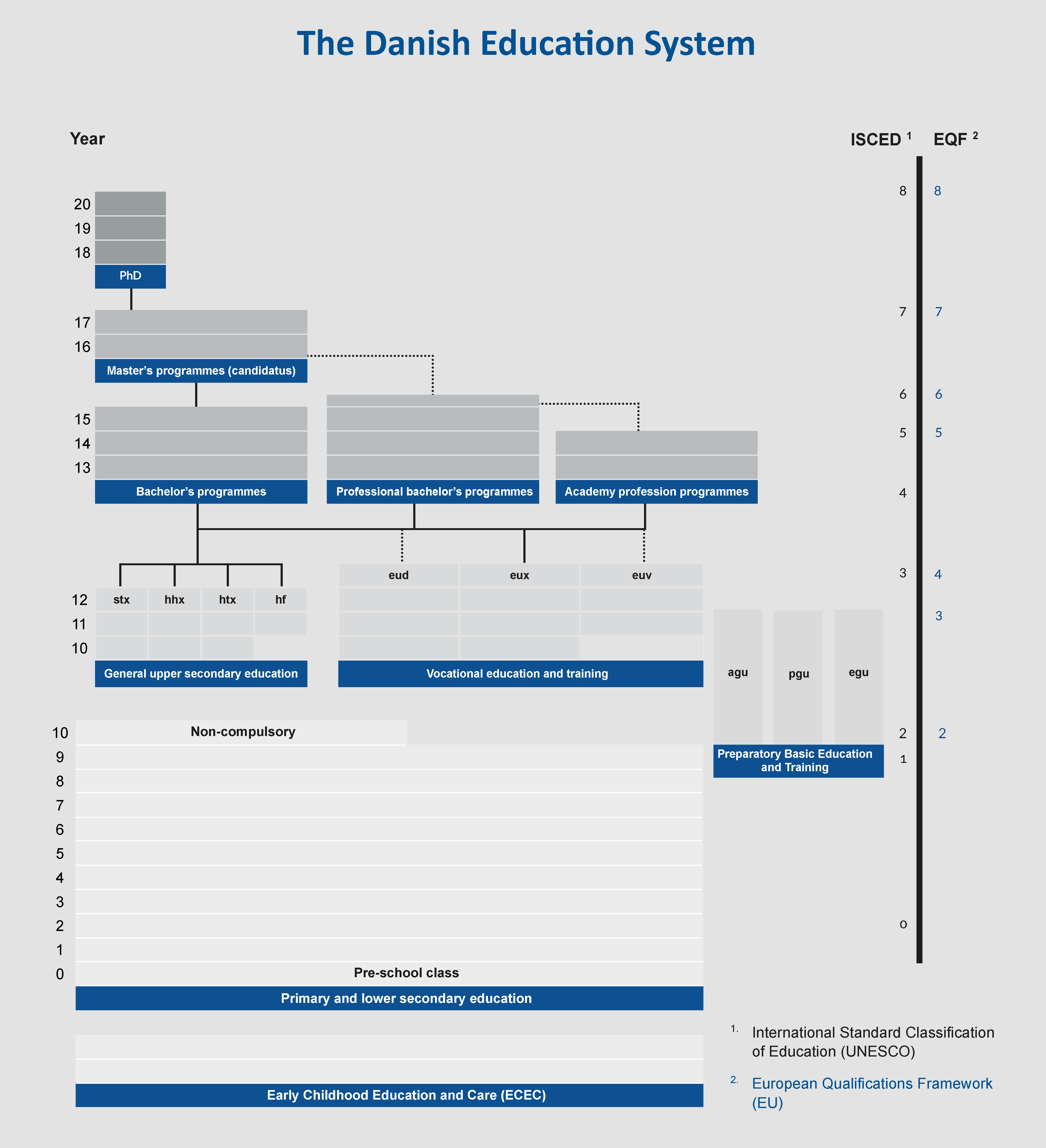
The Danish education structure
Early childhood education and care (ECEC)
ECEC is for children from 26 weeks (six months) to six years. In Denmark, ECEC is optional, but a majority of children attends it.
The public ECEC institutions comprise:
- Nursery: The children’s age spans from 26 weeks to three years old;
- Kindergarten: The children’s age spans from three to five or six years old;
- Age-integrated institution: The children’s age spans from 26 weeks to five or six years old.
For more information about the institutions, please consult chapter 4.2.
Primary and lower secondary education
The Danish Folkeskole covers primary and lower secondary education. The duration of compulsory primary and lower secondary education is ten years. The pupils are between the age of six and 16.
The primary and lower secondary education institutions comprise:
- Municipal primary and lower secondary schools (Folkeskole);
- Private schools;
- Continuation schools.
For further information, please visit chapter 5.
Upper secondary education
Upper secondary education covers general and vocational upper secondary education. Generally, students start at age 16.
The main pathways comprise:
- General upper secondary education programmes (STX, HHX, HTX, and hf) offered at general upper secondary institutions. Generally, the students attend the programmes when they are 16-19 years old;
- Vocational education and training programmes offered at vocational colleges. The age distribution and the grouping of students depends on the individual VET programme. The average age of students starting on a VET programme is 24 years. Generally, the programmes are completed after three to five years.
For further information, please visit chapter 6.
Higher education
Higher education covers short, first, second, and third cycle higher education. Students need an upper secondary school leaving certificate to attend higher education. Generally, the students start at age 19.
Short cycle higher education:
- Academy Profession programmes are offered at the business academies. Generally, the programme is completed after two years.
First cycle higher education:
- Professional bachelor’s degree programmes are offered at the university colleges. Generally, the programme is completed after three and a half years;
- University bachelor’s degree programmes are offered at the universities. Generally, the programme is completed after three years.
Second cycle higher education:
- Master’s degree programmes are offered at the universities and are generally completed after two years.
Third cycle higher education:
- PhD programmes are offered at the universities and are generally completed after three years.
For further information, please visit chapter 7.1.
Adult education and training
Generally, the adult education system offers programmes equivalent to those in the ordinary education system. Adult education programmes can be divided into the following categories:
- General adult education: FVU, AVU, and hf;
- Vocationally oriented education: AMU and euv;
- Professional and Vocational Adult Education: Academy profession (part-time) programmes, diploma programmes, and master programmes;
- Non-formal adult education: Day Folk High Schools, Evening Schools etc.
For further information, please consult chapter 8.3.
The Danish education system